-
What happened?
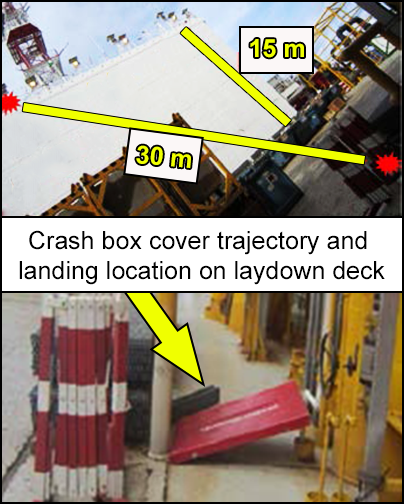
A 7kg crash kit box cover was dislodged by the downwash of a landing helicopter.
The cover was blown over the handrails and fell 15 metres/50 feet to a laydown deck.
Nobody was injured as the laydown area was clear at the time, but this could have caused severe injury or fatality. Foreign object debris (FODs) can even potentially cause damage to the aircraft.
-
Why did it happen?
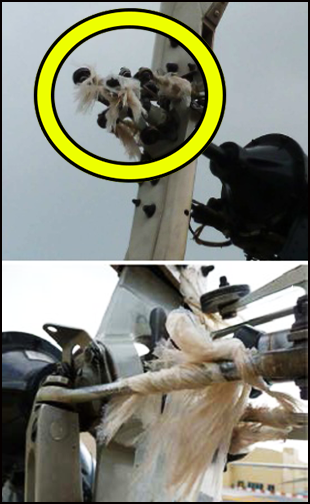
The crash kit box design did not include hinges.
Latches securing the cover of the crash box were loose as no seals were installed.
Lack of inspection.

-
What did they learn?
FODs can cause damage to aircraft. They are a recognised cause of incidents.
Examples of FODs: stones, metal objects, materials (wood, ice, snow, sprays, plastics, animals).
Ensure the person in charge of landing/take-off is trained appropriately.
Ensure the landing/take-off area is systematically inspected daily before all landings/take-offs.
Thorough housekeeping on and around the helideck is essential as FODs can be dislodged by the downwash.
All objects in the vicinity of helidecks must be properly secured.
Identify and report any FODs to avoid incidents.
-
Ask yourself or your crew
How can something like this happen here and what can we do to prevent it?
Why do you think that lid was not secured?
How do we know if the helideck area and vicinity is thoroughly inspected and FOD-free?
What do you do if you spot an unsecured object or potential foreign debris? Who do you report it to?

Add to homescreen
Content name
Select existing category:
Content name
New collection
Edit collection
What happened?
A 7kg crash kit box cover was dislodged by the downwash of a landing helicopter.
The cover was blown over the handrails and fell 15 metres/50 feet to a laydown deck.
Nobody was injured as the laydown area was clear at the time, but this could have caused severe injury or fatality. Foreign object debris (FODs) can even potentially cause damage to the aircraft.

Why did it happen?
The crash kit box design did not include hinges.
Latches securing the cover of the crash box were loose as no seals were installed.
Lack of inspection.

What did they learn?
FODs can cause damage to aircraft. They are a recognised cause of incidents.
Examples of FODs: stones, metal objects, materials (wood, ice, snow, sprays, plastics, animals).
Ensure the person in charge of landing/take-off is trained appropriately.
Ensure the landing/take-off area is systematically inspected daily before all landings/take-offs.
Thorough housekeeping on and around the helideck is essential as FODs can be dislodged by the downwash.
All objects in the vicinity of helidecks must be properly secured.
Identify and report any FODs to avoid incidents.

Ask yourself or your crew
How can something like this happen here and what can we do to prevent it?
Why do you think that lid was not secured?
How do we know if the helideck area and vicinity is thoroughly inspected and FOD-free?
What do you do if you spot an unsecured object or potential foreign debris? Who do you report it to?
A 7kg crash kit box cover was dislodged by the downwash of a landing helicopter and blown over 15 metres to a laydown deck. Nobody was injured as the laydown area was clear at the time.