-
Quiz
Q1. Are you more likely to fall off a ladder when ascending (going up) or descending (going down)?
Q2. How high are most falls from ladders?
Q3. What things contribute to falls from ladders?

-
Answers
A1. 98% of ladder falls happen while descending (going down) the ladder.
A2. 74% of falls happen less that 6 feet from the ground.
30% of falls happen while stepping off the bottom rung.
A3. Encourage your team to talk about the things that affect them.
Other factors include:
- Environmental (oil, rain, wet gloves)
- This is a routine task, performed daily. People become too used to the risk
- Transition to/from platform and ladder also contributes

-
What can we learn?
Recognise the danger from descending ladders:
Injury is more likely when descending.
Give 100% focus on transitioning and descending until both feet firmly on the ground/grade.
Understand the risk of environmental factors (e.g. rain and oil).
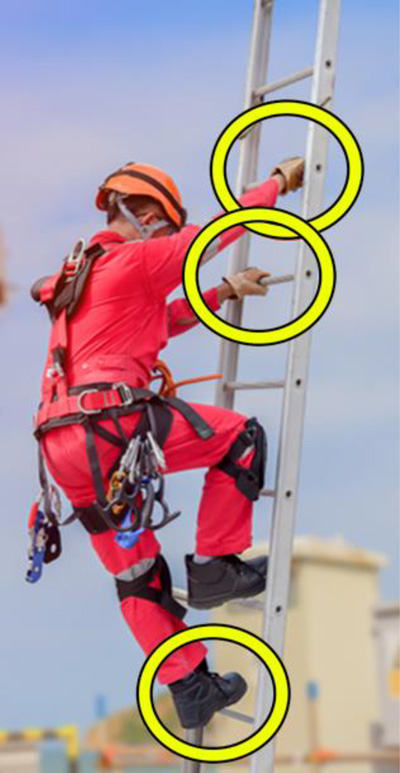
Three points of contact at all times:
It takes effort to practice, slow down and ensure a constant 3-points of contact.
100% focus on 3-points of contact wile climbing or descending.
When descending, a missed step results in two or less points of contact and a higher change for fall to occur.
Higher exposure exists when…
…climbing vertical (90 degree) ladders (i.e. scaffold ladder) versus inclined ladders.
…taking the last few steps prior to disembarking the ladder.

-
Ask yourself or your crew
Why do you think it is riskier to climb down a ladder than climb up it?
Share an experience when you fell, or nearly fell, from a ladder. Why did it happen?
What changes can we make to how we work to prevent falls from ladders?

Add to homescreen
Content name
Select existing category:
Content name
New collection
Edit collection
Quiz
Q1. Are you more likely to fall off a ladder when ascending (going up) or descending (going down)?
Q2. How high are most falls from ladders?
Q3. What things contribute to falls from ladders?
Answers
A1. 98% of ladder falls happen while descending (going down) the ladder.
A2. 74% of falls happen less that 6 feet from the ground.
30% of falls happen while stepping off the bottom rung.
A3. Encourage your team to talk about the things that affect them.
Other factors include:
- Environmental (oil, rain, wet gloves)
- This is a routine task, performed daily. People become too used to the risk
- Transition to/from platform and ladder also contributes
What can we learn?
Recognise the danger from descending ladders:
Injury is more likely when descending.
Give 100% focus on transitioning and descending until both feet firmly on the ground/grade.
Understand the risk of environmental factors (e.g. rain and oil).
Three points of contact at all times:
It takes effort to practice, slow down and ensure a constant 3-points of contact.
100% focus on 3-points of contact wile climbing or descending.
When descending, a missed step results in two or less points of contact and a higher change for fall to occur.
Higher exposure exists when…
…climbing vertical (90 degree) ladders (i.e. scaffold ladder) versus inclined ladders.
…taking the last few steps prior to disembarking the ladder.

Ask yourself or your crew
Why do you think it is riskier to climb down a ladder than climb up it?
Share an experience when you fell, or nearly fell, from a ladder. Why did it happen?
What changes can we make to how we work to prevent falls from ladders?
Descending ladders is a routine task, performed daily, to which individuals became too used to the risk. This case study looks at the dangers from descending ladders and the factors that influence it.