-
What happened?
A 37m (120ft) concrete placing boom was being used.
A weld in the top of the boom crane cracked.
The crack spread down to the boom’s side plates.
The first boom stage (truck end) of the crane collapsed onto a house roof.
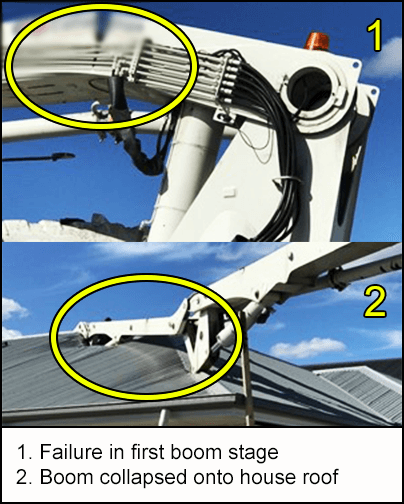
-
Why did it happen?
The failure was mainly a result of weld fatigue.
The weld connecting the semi-circular stiffening section to the boom top plate cracked.
The crack spread down the side plate and the boom broke.
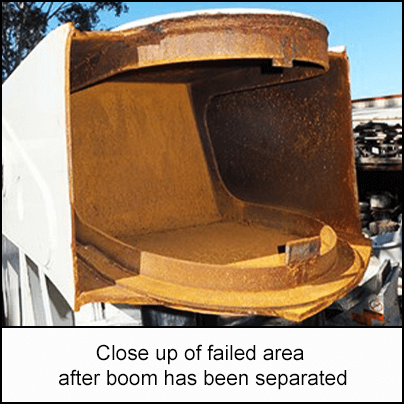

-
What did they learn?
Carry out extra inspections of the booms to check for:
- the appearance of cracks and other defects, especially in welded connections and other high stress areas.
- deformation of the boom including buckling of boom plates, and impact damage.
- indications of corrosion including internal corrosion.
If a defect is found, it should be referred to the manufacturer.
Extra health and safety guidance should be followed when using concrete placing booms.

-
Ask yourself or your crew
If this happened to us, what could the consequences be?
How can we be sure something like this won’t happen here? What tests or inspections can we do?
What else could we do to mitigate the risk of this happening?

Add to homescreen
Content name
Select existing category:
Content name
New collection
Edit collection
What happened?
A 37m (120ft) concrete placing boom was being used.
A weld in the top of the boom crane cracked.
The crack spread down to the boom’s side plates.
The first boom stage (truck end) of the crane collapsed onto a house roof.

Why did it happen?
The failure was mainly a result of weld fatigue.
The weld connecting the semi-circular stiffening section to the boom top plate cracked.
The crack spread down the side plate and the boom broke.

What did they learn?
Carry out extra inspections of the booms to check for:
- the appearance of cracks and other defects, especially in welded connections and other high stress areas.
- deformation of the boom including buckling of boom plates, and impact damage.
- indications of corrosion including internal corrosion.
If a defect is found, it should be referred to the manufacturer.
Extra health and safety guidance should be followed when using concrete placing booms.
Ask yourself or your crew
If this happened to us, what could the consequences be?
How can we be sure something like this won’t happen here? What tests or inspections can we do?
What else could we do to mitigate the risk of this happening?
A boom crane was being used when the boom cracked due to a weld failure. The boom collapsed onto a house roof.