-
What happened?
A well was placed on emergency shut down (ESD) due to high pressure in the pipeline.
To maintain the wellhead flowing temperatures, it was decided to use temporary flowback equipment.
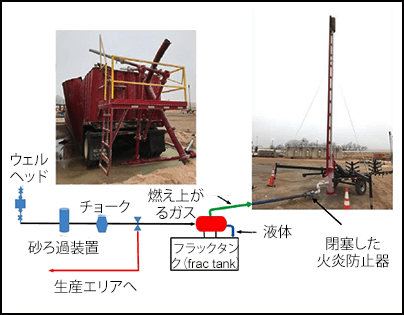
The flow was started through the temporary equipment (knockout vessel, frac tank, flare piping and flare stack).
45 minutes later, the flare started to flicker, and within the next 15 minutes, the knockout drum ruptured.
ESD was activated and the well was secured using the master valve.
Workers were shut in the well, but fortunately no one was injured.
-
Why did it happen?
An ice plug formed in the flare line piping. Ice was observed downstream of the flame arrestor, and an ice sheet on the bottom shell of the knockout drum.
Well flowback characteristics differed from expectations.
A change in operations (i.e. inability to send gas production and sales) was managed by using the available flowback equipment without understanding the design limitations of the equipment.
-
What did they learn?
Include temporary flowback equipment and operating scenarios during hazard and operability studies (HAZOP).
- Recognise that workers may need more instruction on new well flowback characteristics.
Establish processes for design, selection and acceptance of temporary flowback equipment to include:
- Develop detailed operating procedures including flowback equipment operating limits.
- Verify procedures are communicated effectively to operations personnel.
Confirm operating personnel can describe operating limits and execute operating procedures.

-
Ask yourself or your crew
What is the worst that could have happened?
How could this incident have been prevented?
Do you check for ice formations on the equipment you work with? If not, should you?
What are the hazards associated with using temporary flowback equipment?
Are you trained to perform your tasks? What should you do if you require additional training?

Add to homescreen
Content name
Select existing category:
Content name
New collection
Edit collection
What happened?
A well was placed on emergency shut down (ESD) due to high pressure in the pipeline.
To maintain the wellhead flowing temperatures, it was decided to use temporary flowback equipment.
The flow was started through the temporary equipment (knockout vessel, frac tank, flare piping and flare stack).
45 minutes later, the flare started to flicker, and within the next 15 minutes, the knockout drum ruptured.
ESD was activated and the well was secured using the master valve.
Workers were shut in the well, but fortunately no one was injured.
Why did it happen?
An ice plug formed in the flare line piping. Ice was observed downstream of the flame arrestor, and an ice sheet on the bottom shell of the knockout drum.
Well flowback characteristics differed from expectations.
A change in operations (i.e. inability to send gas production and sales) was managed by using the available flowback equipment without understanding the design limitations of the equipment.

What did they learn?
Include temporary flowback equipment and operating scenarios during hazard and operability studies (HAZOP).
- Recognise that workers may need more instruction on new well flowback characteristics.
Establish processes for design, selection and acceptance of temporary flowback equipment to include:
- Develop detailed operating procedures including flowback equipment operating limits.
- Verify procedures are communicated effectively to operations personnel.
Confirm operating personnel can describe operating limits and execute operating procedures.
Ask yourself or your crew
What is the worst that could have happened?
How could this incident have been prevented?
Do you check for ice formations on the equipment you work with? If not, should you?
What are the hazards associated with using temporary flowback equipment?
Are you trained to perform your tasks? What should you do if you require additional training?
A well was placed on emergency shut down (ESD) due to high pressure in the pipeline. Temporary flowback equipment was being used, when the flare started to flicker and the knockout drum was ruptured.