-
What happened?
A crude unit vacuum furnace suffered a flameout and subsequent re-ignition.
The unit normally operates on fuel gas supplemented with natural gas.
It was discovered that the furnace was firing 100% natural gas during the shutdown process.

-
Why did it happen?
Fuel gas pressure was too high for natural gas firing, leading to a flameout.
Burners were not designed for running solely on lower pressure natural gas versus higher pressure fuel gas.
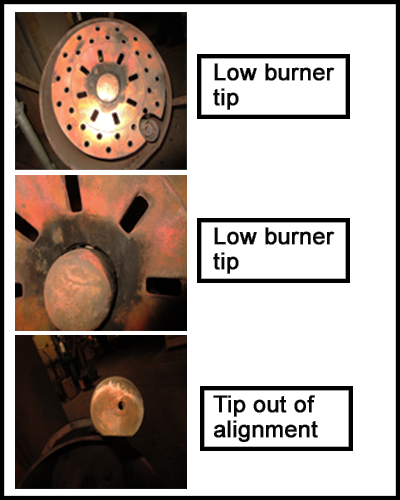
Low burner tips and one tip out of alignment contributed to flame instability.
Burner curves on natural gas were not reflected in the safe operating limits and trip parameters.
-
What did they learn?
Modify shutdown procedures to ensure heaters do not fire on high-percentage of natural gas.
Modify safe operating limits and trip parameters to reflect burner curves on natural gas.
Develop a calculation to determine percentage natural gas in the fuel and provide alarms in the distributed control system.
Set heater operating guidelines for high natural gas feed.

-
Ask yourself or your crew
What actions could have been taken?
Why do we think this happened during shutdown?
How could something like this happen here?
What would be the potential consequences of a flameout here?
How do we know we are using the right fuel mixture?

Add to homescreen
Content name
Select existing category:
Content name
New collection
Edit collection
What happened?
A crude unit vacuum furnace suffered a flameout and subsequent re-ignition.
The unit normally operates on fuel gas supplemented with natural gas.
It was discovered that the furnace was firing 100% natural gas during the shutdown process.

Why did it happen?
Fuel gas pressure was too high for natural gas firing, leading to a flameout.
Burners were not designed for running solely on lower pressure natural gas versus higher pressure fuel gas.
Low burner tips and one tip out of alignment contributed to flame instability.
Burner curves on natural gas were not reflected in the safe operating limits and trip parameters.

What did they learn?
Modify shutdown procedures to ensure heaters do not fire on high-percentage of natural gas.
Modify safe operating limits and trip parameters to reflect burner curves on natural gas.
Develop a calculation to determine percentage natural gas in the fuel and provide alarms in the distributed control system.
Set heater operating guidelines for high natural gas feed.
Ask yourself or your crew
What actions could have been taken?
Why do we think this happened during shutdown?
How could something like this happen here?
What would be the potential consequences of a flameout here?
How do we know we are using the right fuel mixture?
A crude unit vacuum furnace suffered a flame out and subsequent reignition. Fuel gas pressure was too high for natural gas firing, leading to a flameout.